In today’s increasingly digital world, the need for robust cybersecurity measures has never been greater. With the rise of cyber threats such as ransomware, malware, and social engineering attacks, organizations are constantly on the lookout for ways to protect their valuable assets and sensitive data.
One such solution is the Intrusion Detection and Prevention System (IDPS). An IDPS is a security solution that helps organizations detect and prevent potential cyber attacks before they can do harm. By monitoring network traffic and identifying suspicious activity, an IDPS can provide organizations with the peace of mind they need to focus on their core operations.
But as cyber threats continue to evolve and become more sophisticated, the capabilities of IDPS solutions will need to keep pace. In this article, we will explore the future of IDPS and how it will need to adapt to remain effective in preventing and detecting cyber attacks.
We will delve into the latest trends in IDPS, such as the use of machine learning and artificial intelligence, and how they can improve detection accuracy and automate response. We will also examine the integration of IDPS solutions with other security solutions such as SIEM and EDR to provide a more comprehensive view of an organization’s security posture.
Additionally, we will explore the unique challenges presented by the Internet of Things (IoT), and how IDPS solutions will need to be able to detect and prevent attacks on these devices.
Finally, we will examine the need for IDPS solutions to be agile and adaptable in order to keep up with the changing threat landscape. We will discuss the use of threat intelligence feeds and advanced analytics to provide real-time threat detection and response.
This article will provide a comprehensive overview of the future of IDPS and how it will need to adapt to remain effective in the face of evolving cyber threats. Whether you are an IT professional, business owner, or simply interested in cybersecurity, this article is a must-read for anyone who wants to stay ahead of potential threats and protect their valuable assets.
What is Intrusion Detection System?
An Intrusion Detection System (IDS) is a security solution that monitors network traffic and identifies any malicious activity or intrusion. It can detect a wide range of attacks, including malware, brute force attacks, and DoS attacks. IDS solutions can be either host-based, where they monitor activity on a specific device, or network-based, where they analyze traffic across the entire network.
Imagine that you are the guardian of a fortified castle. Your job is to keep the castle safe from any intruders who may try to breach its walls and harm its inhabitants. You have archers stationed on the walls who are constantly on the lookout for any suspicious activity, and guards at the gates who verify the identity of anyone who wants to enter.
Similarly, an Intrusion Detection System (IDS) is like a digital guardian for a computer network. Its job is to monitor the network and look for any suspicious activity that may indicate an intruder attempting to breach its defenses. Just like the archers on the castle walls, an IDS uses advanced techniques such as signature-based detection, anomaly detection, and protocol analysis to identify potential threats.
But an IDS is not just a passive observer. It is also like the guards stationed at the castle gates who take action to prevent any unauthorized access. If an IDS detects any malicious activity, it can alert security personnel, block traffic from the attacker’s IP address, or even shut down the entire network to prevent further damage.
In essence, an IDS is the digital equivalent of a vigilant guardian, constantly on the lookout for any potential threats and ready to take action to protect the network from harm. Just like the castle guardian, an IDS is an essential component of a strong defense system, helping to keep sensitive information and valuable assets safe from harm.
What is Intrusion Prevention System?
An Intrusion Prevention System (IPS) is a network security solution designed to identify and block potential threats before they can do harm. IPS solutions build on the capabilities of Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS), by not only detecting potential threats but also taking action to prevent them.
An IPS solution operates by analyzing network traffic, looking for patterns or behavior that may indicate a threat. Once a potential threat is identified, the IPS can take a variety of actions to prevent it from doing any harm. This can include blocking traffic from the source of the threat, quarantining potentially infected devices, or even shutting down the entire network to prevent further damage.
IPS solutions are typically deployed at the network perimeter, providing an additional layer of defense against external threats. They can be integrated with other security solutions, such as firewalls and antivirus software, to provide comprehensive security coverage. Some IPS solutions can also be deployed on individual devices, providing protection against internal threats or attacks that originate from compromised devices.
How Intrusion Detection System Works

The primary goal of IDS is to detect anomalies before cybercriminals damage the network and its associated devices. IDS tools use a database of known attack signatures or information about deviations from regular network activities to trace anomalies.
The system then pushes up these anomalies and deviation detection information for review and evaluation at the application layer and network level. IDS internal working gets managed by three different components. These are:
- Sensors that analyze network activities and traffic to trigger security events.
- Console that monitors events to send alerts and notifications while managing the response and report generation.
- Detection Engine records all the alerts, notifications, and actions related to security events and registers them in a separate database.
In addition to its components, IDS have four different approaches to detecting malicious traffic, which are as follows:
- Signatures:IDS can detect attack patterns by comparing signatures against the network packet content.
- Anomalies:Modern IDS systems use machine learning techniques to detect anomalies in network traffic or data packets. The ML algorithm learns from regular network activities.
- Unauthorized access:Security professionals configure the Access Control Lists (ACLs) in IDS to detect and verify user requests. The IDS checks all access requests against ACLs.
- Protocol-based anomaly:IDS can also detect malicious activities and anomalies in protocols. If any protocols used within the network do not meet the standards configured within the IDS, it will generate notifications and alerts.
How Intrusion Prevention System Works
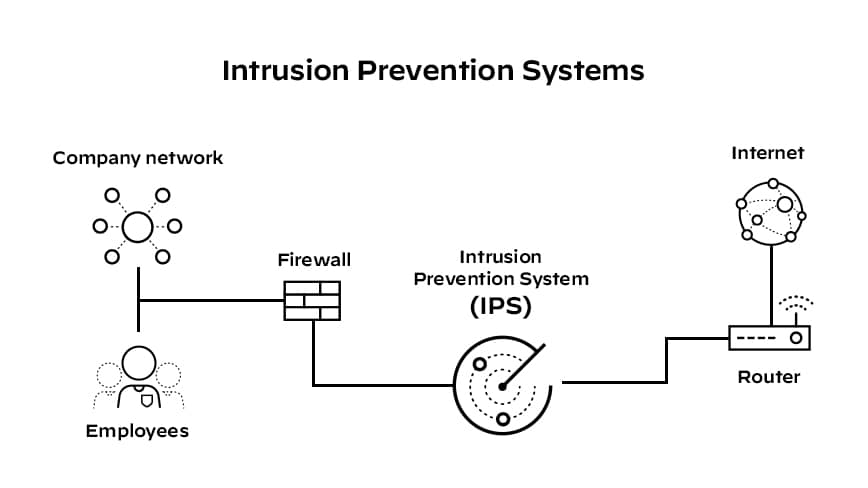
The IPS is placed inline, directly in the flow of network traffic between the source and destination. This is what differentiates IPS from its predecessor, the intrusion detection system (IDS). Conversely, IDS is a passive system that scans traffic and reports back on threats.
Usually sitting right behind the firewall, the solution analyzes all traffic flows that enter the network and takes automated actions when necessary.
These actions can include:
- Sending an alarm to the administrator (as would be seen in an IDS)
- Dropping the malicious packets
- Blocking traffic from the source address
- Resetting the connection
- Configuring firewalls to prevent future attacks
As an inline security component, the IPS must be able to:
- Work efficiently to avoid degrading network performance
- Work fast, because exploits can happen in near-real time
- Detect and respond accurately to eliminate threats and false positives (i.e., legitimate packets misread as threats).
To do this successfully, there are several techniques used for finding exploits and protecting the network from unauthorized access. These include:
- Signature-based detection is a detection method based on a dictionary of uniquely identifiable patterns (or signatures) in the code of each exploit. As an exploit is discovered, its signature is recorded and stored in a continuously growing dictionary of signatures. Signature detection for IPS breaks down into two types:
- Exploit-facing signatures identify individual exploits by triggering on the unique patterns of a particular exploit attempt. The IPS can identify specific exploits by finding a match with an exploit-facing signature in the traffic stream.
- Vulnerability-facing signatures are broader signatures that target the underlying vulnerability in the system that is being targeted. These signatures allow networks to be protected from unidentified. They also raise the risk of false positives.
- Anomaly-based detection takes samples of network traffic at random and compares them to a pre-calculated baseline performance level. When the traffic activity is outside the parameters of baseline performance, the IPS takes action.
- Policy-based detection requires system administrators to configure security policies based on an organization’s security policies and network infrastructure. If any activity occurs that breaks a defined security policy, an alert is triggered and sent to the admins.
Differences between IDS and IPS
The main difference between IDS and IPS is that IDS solutions only detect malicious activity, while IPS solutions detect and prevent it. IDS solutions are useful for detecting attacks and analyzing them to determine their nature and severity. IPS solutions, on the other hand, are useful for preventing attacks in real-time. They can automatically block malicious traffic and prevent attackers from gaining unauthorized access to a system.
Types of Intrusion Detection Systems
These systems are categorized based on activities and methods. Here are four types of intrusion detection systems.
1. Host Intrusion Detection System (HIDS)
HIDS monitors all host devices and computers within the network perimeter. It has direct access to all systems within the network and across the enterprise’s internal network. HIDS can identify internal threats, wherein malicious traffic gets generated from within the host system residing on the network.
2. Network Intrusion Detection System (NIDS)
NIDS gets deployed at strategic points within the network to monitor various network segments in an enterprise. It helps identify malicious activity for outbound and inbound traffic to and from all host devices within the network. NIDS cannot always identify internal threats.
3. Anomaly-based Intrusion Detection System (AIDS)
AIDS works by monitoring and identifying anomalies within the network traffic. Security engineers and professionals establish a baseline to determine what is normal for the enterprise network in terms of protocols, bandwidth, ports, devices used, etc.
4. Signature-based Intrusion Detection System (SIDS)
SIDS works by monitoring and identifying signatures of the data packets traversing within the network. The IDS tool compares the data packets against the database of previously experienced/drawn attack signatures or known malicious attack attributes to issue alerts.
The benefits of using intrusion detection and prevention systems
IDS and IPS solutions offer several benefits to organizations and businesses, including:
- Improved Security: IDS and IPS solutions can help prevent attacks and detect any malicious activity before it can cause harm.
- Reduced Downtime: By preventing attacks and mitigating their impact, IDS and IPS solutions can help reduce system downtime and improve overall system availability.
- Compliance: IDS and IPS solutions can help organizations comply with industry and regulatory requirements, such as PCI DSS and HIPAA.
- Cost Savings: By preventing attacks and minimizing their impact, IDS and IPS solutions can help save organizations money on recovery costs and potential fines.
How do intrusion prevention systems (e.g. Snort) prevent CSRF and XSS attacks?
Intrusion Prevention Systems, such as Snort, can prevent Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF) and Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) attacks by using signature-based detection and anomaly detection.
For CSRF attacks, Snort can detect and prevent them by analyzing HTTP traffic and looking for certain patterns that indicate an attack. These patterns can include unexpected requests or requests that come from untrusted sources. Once an attack is detected, Snort can block the malicious traffic and prevent the attack from succeeding.
For XSS attacks, Snort can detect and prevent them by analyzing HTML and JavaScript code for any suspicious activity. It can identify scripts that attempt to execute malicious code or modify the content of a webpage. Once detected, Snort can remove or block the malicious code and prevent the attack from succeeding.
How to choose the right IDPS for your organization?
Choosing the right IDS or IPS solution for your organization can be challenging. Here are some factors to consider when selecting a solution:
- Scalability: Ensure that the solution can scale to meet the needs of your organization as it grows.
- Customization: Look for a solution that can be customized to meet the specific needs of your organization.
- Integration: Ensure that the solution can integrate with your existing security infrastructure.
- Ease of use: Look for a solution that is easy to deploy, configure, and manage.
- Performance: Ensure that the solution can operate at the required performance levels without affecting system performance.
- Cost: Consider the cost of the solution and ensure that it provides value for money.
The Future of intrusion detection and prevention systems
The future of Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDPS) is promising, as the security landscape continues to evolve and become more complex. As attackers become more sophisticated in their methods, IDPS solutions will need to keep pace to remain effective in preventing and detecting attacks.
One trend in IDPS is the increasing use of machine learning and artificial intelligence. These technologies can help improve detection accuracy by analyzing large volumes of data and identifying patterns that may be difficult to detect using traditional methods. They can also automate response, enabling faster and more effective threat mitigation.
Another trend is the integration of IDPS solutions with other security solutions such as Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) and Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR). By integrating these solutions, organizations can achieve a more comprehensive view of their security posture and respond more quickly to potential threats.
The rise of the Internet of Things (IoT) also presents a significant challenge for IDPS solutions. With billions of IoT devices expected to be connected to the internet, the attack surface for potential threats will be larger than ever before. IDPS solutions will need to be able to detect and prevent attacks on these devices, which may have limited computing power and memory.
Finally, IDPS solutions will need to be agile and adaptable to keep up with the changing threat landscape. This may involve the use of threat intelligence feeds and advanced analytics to provide real-time threat detection and response.
Conclusion
In conclusion, in a world where cyber threats are becoming increasingly sophisticated and prevalent, it’s essential to have robust security measures in place. Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) and Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS) are two such measures that can help organizations stay ahead of potential threats and protect their sensitive data and assets.
IDS solutions act as digital guardians, constantly monitoring network traffic and identifying potential threats. They use advanced techniques such as signature-based detection, anomaly detection, and protocol analysis to detect malicious activity. On the other hand, IPS solutions take it a step further by actively blocking potential threats before they can do any harm.
The benefits of using IDS and IPS solutions are numerous, including improved security, reduced downtime, compliance with regulatory requirements, and cost savings. They also provide valuable insights into network activity, which can be used to identify potential vulnerabilities and improve an organization’s overall security posture.
As cyber threats continue to evolve, IDS and IPS solutions will need to keep pace to remain effective. Future solutions may incorporate advanced technologies such as machine learning and artificial intelligence to improve detection accuracy and automate response.
In the end, it’s important to remember that cyber threats are not going away anytime soon. By implementing robust security measures such as IDS and IPS solutions, organizations can stay one step ahead of potential threats and protect their valuable assets. After all, as the old saying goes, an ounce of prevention is worth a pound of cure.